A study led by the University of Cagliari reveals the secrets of the gamma-ray resistant bacterium
The scientific work published in the "Journal of Biological Chemistry"Per restare aggiornato entra nel nostro canale Whatsapp
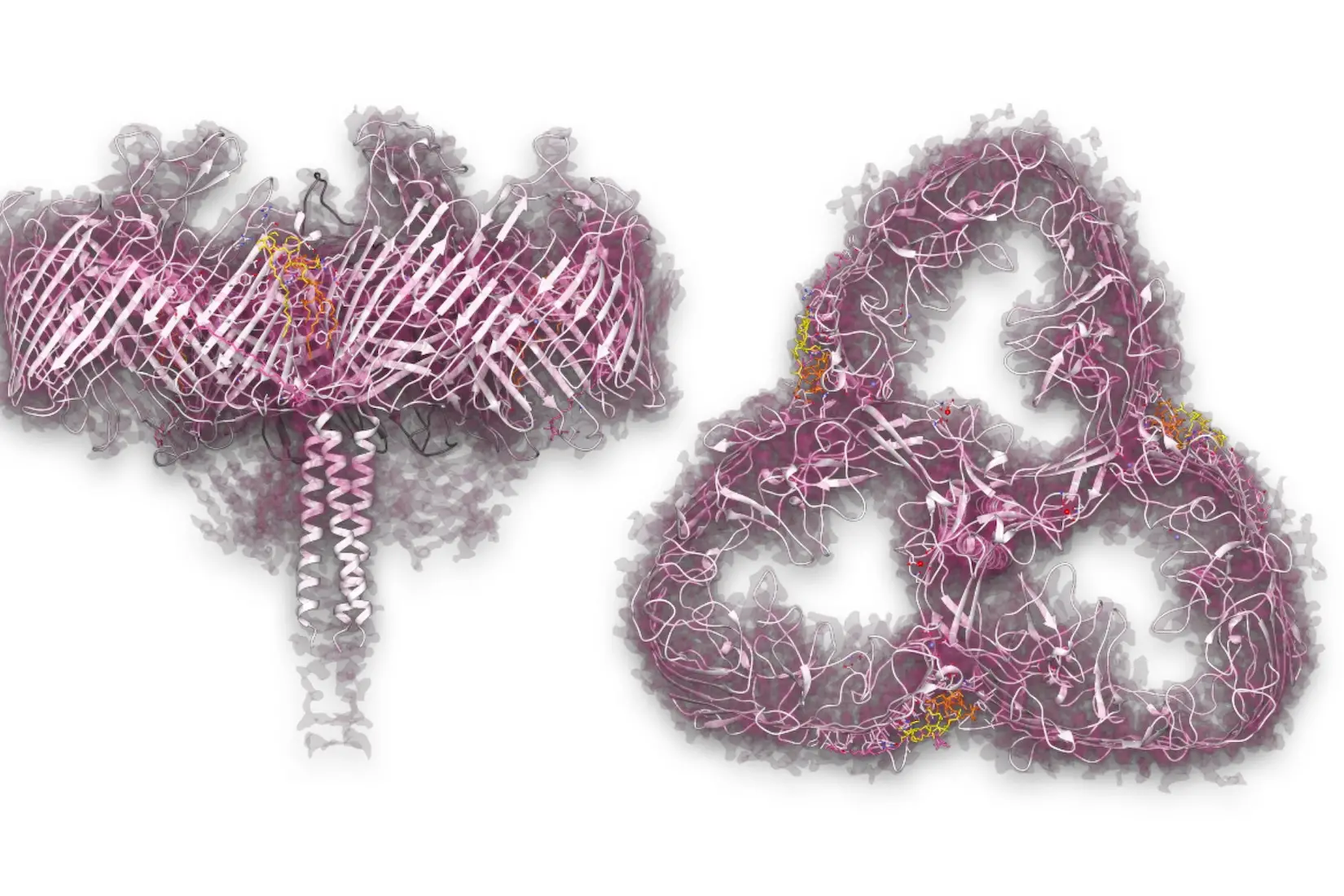
A scientific work that reveals the three-dimensional structure at atomic resolution of one of the major protein complexes of the cell envelope of the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans has been published in the “Journal of Biological Chemistry”.
The research, which concerns the organism able to live in extreme environments with strong ability to resist strong dehydration, heat, and electromagnetic stress, was led by researchers of the University of Cagliari Dario Piano and Domenica Farci, thanks to the funding of the National Science Center (Poland) and involved important European institutions such as Warsaw University of Life Sciences SGGW (Poland), Jacobs University Bremen (Germany), European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (France), Charles University and the Central European Institute of Technology Masaryk University (Czech Republic), and Umeå University (Sweden).
The bacterium in question is currently a unique organism of its kind due to its ability to withstand a dose of gamma radiation 15 thousand times higher than those sufficient to kill a man.
The results obtained from the study may find application in biomedicine for the development of new generation antibiotics and in nanotechnologies for the development of new biomaterials that can be used in photonics and for the production of biosensors.
(Unioneonline / ss)