Fight against coronavirus, a new pharmaceutical target identified at the University of Cagliari
Important scientific study carried out by a team led by Enzo Tramontano
Per restare aggiornato entra nel nostro canale Whatsapp
Important result from the University of Cagliari on the front of the fight against the coronavirus . A team led by Enzo Tramontano has carried out a scientific study that identifies a new pharmaceutical target and the results have been published in the American journal “ACS Pharmacology and Translational Science”.
The value of the research is underlined by the entire cover dedicated to the work resulting from an international collaboration with contributions from Germany and Poland led by Tramontano, head of the Molecular Virology group of the University of Cagliari, with first author Angela Corona, a young researcher of the same research team of the University of the Sardinian capital.
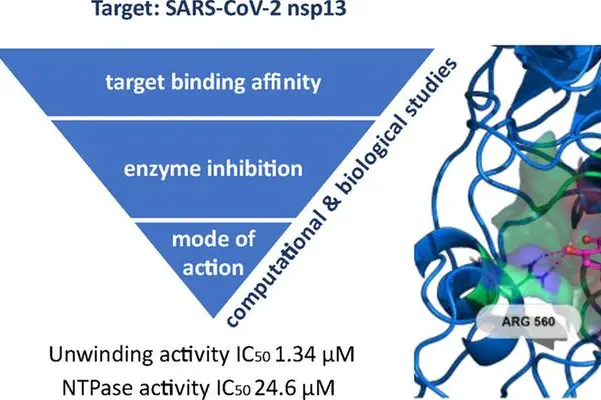
The fulcrum is the development of a system to study the functioning of the viral enzyme helicase, a protein essential for Covid-19 to replicate, and identifies some molecules capable of blocking its catalytic activity at nanomolar concentrations.
“The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic is still raging all over the world - explains Tramontano - and the scientific community is now focusing on new antiviral therapies that can block the infection alongside vaccines. Although still far from clinical use, this is a very important first step in the design of drugs active on this new therapeutic target ".
The research was developed within the international network EXSCALATE4CoV (E4C) funded in 2020 by the European Union within the program to combat SARS-CoV-2, which involved the University of Cagliari, Dompè Farmaceutici SpA, Federico II University of Naples, the International Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology of Warsaw and the Fraunhofer Institute for Translational Medicine and Pharmacology.
(Unioneonline / ss)